Miquela Sousa (@lilmiquela), Shudu (@shudu.gram), and Audy Bleu (@audy.bleu) are social media bots, but not the kind made by the thousands to bestow large quantities of likes on divisive posts. They are carefully crafted CGI characters, two of whom were assumed to be human before their creators opened up about their origin. They are most active on Instagram, although Miquela also releases music available on Spotify. They are also influencers. As of this writing, Miquela has 2 million Instagram followers and over 300,000 monthly listeners on Spotify, Shudu has 200,000 Instagram followers, and Audy Bleu has 200 Instagram followers. In addition to producing content, they are socially interactive, responding to comments and on occasion doing “interviews” with journalists. Virtual influencers are more than just pretty pictures; they are part of the social fabric of the web. How does this affect the health of our online communities? Can virtual influencers be valuable community members, or are they destroying something uniquely human? I argue that bots can contribute to a healthy community when they are honest about their non-human status, fall closer to artistic statements than capitalist emissaries, thoughtfully engage with human identity markers such as race and identity, and encourage discussion between human community members.
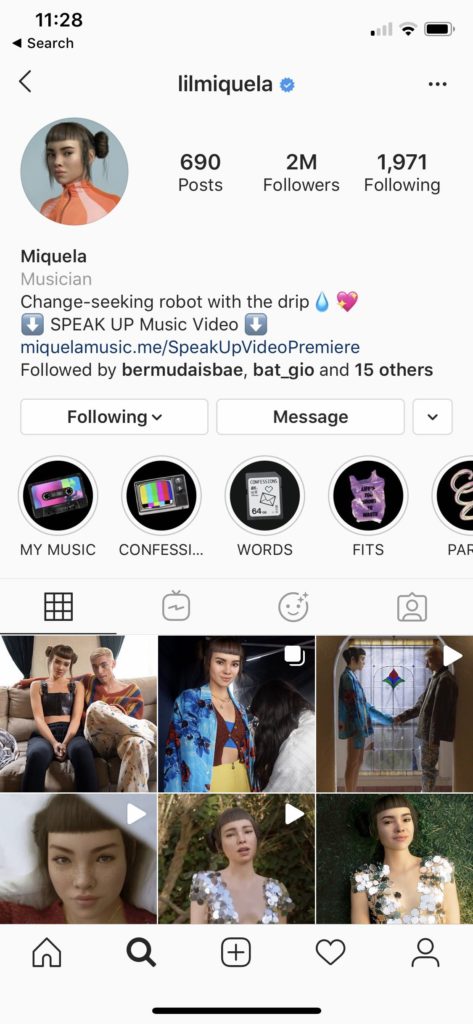
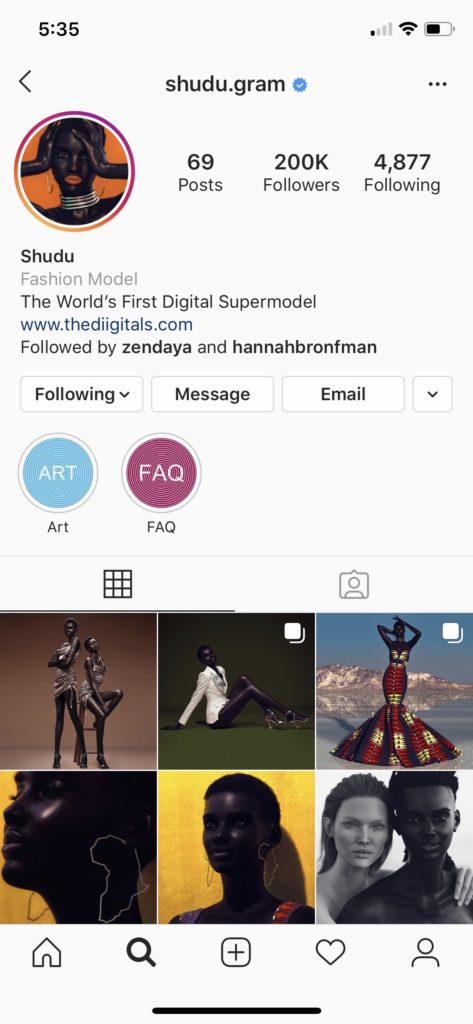
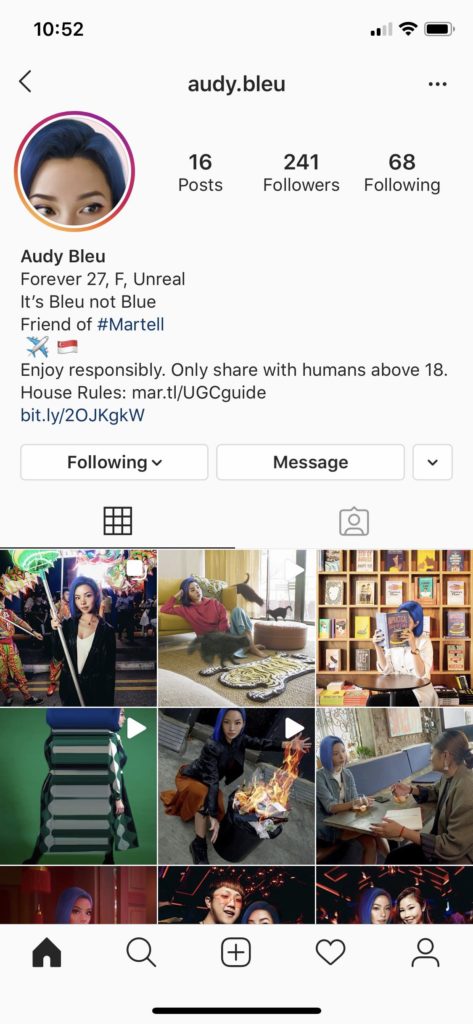
In this article I draw on an investigation of the Instagram accounts of virtual influencers including Miquela, Shudu, and Audy Bleu as well as the ones listed in the table below. I review their posts, comments below posts, and followers. I also do a discourse analysis of numerous online articles about the influencers and their creators (see References section).
| Name | Followers | Creator | Country | Year | |
| Miquela Sousa | @lilmiquela | 2 million | Brud | USA | 2016 |
| Bermuda | @bermudaisbae | 221,000 | Brud | USA | 2016 |
| Blawko | @blawko22 | 158,000 | Brud | USA | 2018 |
| Shudu | @shudu.gram | 200,000 | Cameron James-Wilson (now The Diigitals) | UK | 2017 |
| Audy Bleu | @audy.bleu | 200 | Martell (alcohol brand) | Singapore | 2019 |
| War Nymph | @warnymph | 73,800 | Grimes (musician) | USA | 2020 |
| Hatsune Miku | @mikuhatsune | 82,200 | Crypton Future Media | Japan | 2007 |
| Colonel Sanders | @kfc | 1.6 million | Kentucky Fried Chicken | USA | 2019 |
Friends and colleagues often display mild disgust towards the idea of following a bot on social media. I will argue here that virtual community members are not in and of themselves problematic, but they are problematic when masquerading as an actual human. As one reporter remarked, “Shudu is notable for being post-uncanny valley, appearing so human that most people, even with a closer look, wouldn’t suspect that she’s CGI.” (“Shudu, the First Digital Supermodel” 2018) The creators of both Shudu and Miquela initially hid their origins. One of Shudu’s early images, in which she is wearing Rhianna’s beauty brand Fenty, went viral and threw the fashion world into a frenzy trying to uncover her identity. Slowly, Shudu’s creator Cameron James-Wilson came forward saying that it was an art project (“Shudu, the First Digital Supermodel” 2018). He faced both enthusiasm and backlash, much of it centered around whether a white British man should be allowed to create an African digital model (“Photographer Gets Accused Of Racism” 2018).
Brud, the company behind Miquela, Bermuda, and Blawko, went a step further. They released both Miquela and Bermuda in 2016 without any explanation or link to Brud. Miquela, the 19-year-old musician, became particularly popular and garnered hundreds of thousands of followers who presumably believed she represented a human. In April 2018, Brud staged a faux online drama in which Bermuda “took over” Miquela’s account and deleted all her photos, saying that she needed to tell the world the truth. After fanning the internet flames, Brud stepped forward as the creator of both Miquela and Bermuda, and people realized the entire episode had been a carefully curated scam to generate attention (Petrarca 2018). The internet community was angry, but Miquela has continued to gather followers and has over 2 million to date.
Both Shudu and Miquela’s introduction to the world upset their online community. People felt betrayed and lied to. Now that their identities are out in the open, people are able to reconnect as they see fit. It allows for the honest evaluation of a relationship with a robot instead of one founded on deceit. In a world where Facebook deactivates Native American’s accounts because their names don’t sound “real” and refuses to let humans choose their own gender identity (Haimson & Hoffmann 2016), it feels ironic that virtual avatars can now masquerade as real humans on social media platforms. While they may be valuable contributors in their own ways, they clearly shouldn’t be equated with human communication partners.
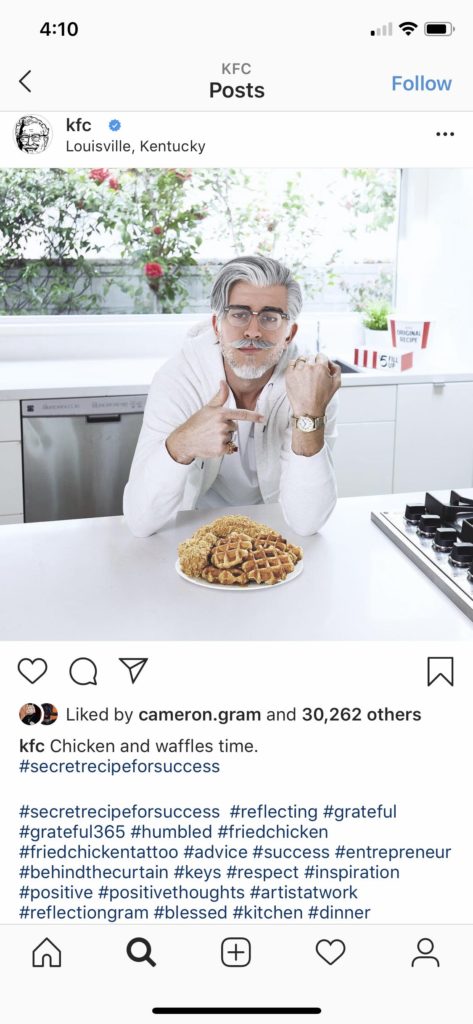
In addition to being honest about their human-ness, virtual community members, like human influencers, should be open about their commercial and brand affiliations. Lifelike bots fall on a spectrum between serving artistic needs and serving capitalist needs. It matters for the health of the community which end of the spectrum a bot falls on, and how honest they are about their purpose. Bots such as Colonel Sanders, who the internet described as Kentucky Fried Chicken’s “hot” logo, and Audy Bleu, who represents the alcohol company Martell, both embody a brand. Kentucky Fried Chicken was completely open about Colonel Sanders and promoted him via their Twitter and Instagram pages (Wright 2019). Audy Bleu’s Instagram profile is more covert but reads “Friend of #Martell” and includes a link to Martell’s website. Cameron James-Wilson claims, on the other hand, that Shudu is an art project. Shudu does occasionally partner with brands, but this is always very clear in the post comments and James-Wilson says in an interview from 2018, “I don’t really see Shudu as a money spinner or a business for me. It’s more of an expression, and when I’ve had companies approach me, if what they want doesn’t reflect in what I see for her then it’s a no go. You know it doesn’t matter about the money or things like that. Because it’s not why I started Shudu. I started her for me, to express myself.” (“Shudu, the First Digital Supermodel” 2018)

What lies in between openly embodied brands and art is murkier, and I argue, more problematic. Human influencers already face this issue to some extent: how to be authentic while taking money from brands to promote certain products. Virtual influencers face the same problem, but it is messier when the influencer is not actually represented by a single human being. Brud’s Miquela, Bermuda, and Blawko clearly fall into this category. Brud’s website claims that it is “a transmedia studio that creates digital character driven story worlds” (“💖 website_copy_wip_for_all_my_qtz 💖” n.d.). However, it has recently raised $20 to $30 million from venture capital firms, and the business model seems to be advertising (Shieber 2019). Miquela has already posted pictures promoting brands like Calvin Klein and Prada. I argue that while similar to a human influencer, this is more problematic for digital influencers. At the end of the day, a human influencer has some degree of agency. This may be limited due to financial constraints, brand pressure, or other factors but it doesn’t disappear completely. If a human feels like something is truly wrong and has a platform with millions of followers, they have the capacity to speak out. A virtual avatar does not. Virtual influencers can be bent in any way a brand desires without putting up a fight. It is for this reason that virtual community members like Miquela who claim to be art but function as capitalist mouthpieces are highly unhealthy for online communities. Openly embodied brands do not hold great potential for helping a community, but they are less damaging than covert marketing machines. On the flip side, virtual community members who strongly limit advertising or steer clear of it entirely and are honest about their non-personhood can be intriguing and fun, in the way fantasy characters have been in novels and stories for far longer than the internet has existed.
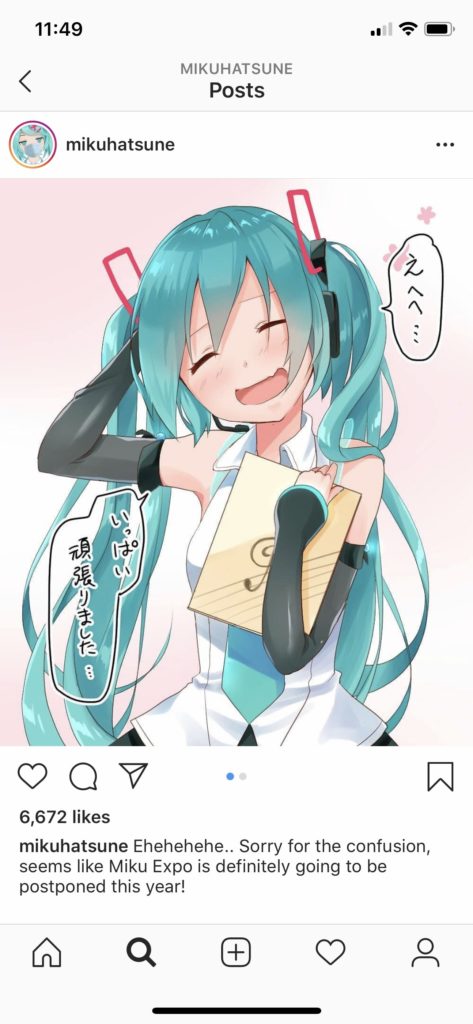
Like story characters before them, social media bots must also contend with issues of human identity, such as race and gender. While many robots, like Amazon Alexa and Google Home, are notorious for evading questions of race and gender, virtual influencers must engage with these to some degree because of their hyper-realistic imagery. Miquela says she is half-Brazilian, half-Spanish (Boshier 2020). Bermuda is Caucasian and blonde. Shudu’s creator cites Princess of South Africa Barbie as his inspiration for the dark-skinned supermodel (B 2019). Audy Bleu has been dubbed Singapore’s first virtual influencer (Thiyagarajan 2020). Hatsune Miku is Japanese (Wikipedia). They are all women. The only male virtual influencers I came across were Blawko, made by Brud, and Colonel Sanders of KFC. Blawko always wears a mask obscuring the lower half of his face. Colonel Sanders is Caucasian.
It matters how virtual character’s identity is designed and displayed since this can either foster an inclusive community or hurt particular groups of real humans. Digital assistant’s front of “neutrality” (despite obvious predilections towards white, female identities) seems to stem from the idea that an “unraced” technology will fit into everyone’s homes. Virtual influencers take a decidedly different approach, recognizing that online communities reflect distinct cultures, in which race and gender are a factor. Using identities to celebrate diversity can lift up communities, but using identities, particularly marginalized identities, to sell products is harmful. In one of Miquela’s Instagram posts, she says “I’m not sure I can comfortably identify as a woman of color. ‘Brown’ was a choice made by a corporation. ‘Woman’ was an option on a computer screen. My identity was a choice Brud made in order to sell me to brands, to appear ‘woke.’ I will never forgive them. I don’t know if I will ever forgive myself. There it is for the digital universe to feast upon: an unabashed staging of diversity without the actual presence of people of color.” This post is surprisingly self-critical and shows Brud grappling publicly with Miquela’s identity. It is perhaps a form of apology to the outraged internet over their lies about her origin. Despite the soul searching, though, Brud continues to use Miquela as a marketing tool. As Rosa Boshier writes for Bitch Media:
In “Feeling Ancestral,” an essay that appears in the 2015 anthology Racial Feelings: Asian America in a Capitalist Culture of Emotion, Santa Ana writes that “the commodification of racial mixture allows us to feel the euphoria of consuming social change while simultaneously forgetting our melancholic past.” Miquela’s easily digestible version of mestizaje offers a glimpse into an alternative universe where implication and culpability don’t exist, erasing any trace of colonial violence and historical oppression. As a simulated influencer with an ever-growing following and brands behind her, ready to pay for access to a relatable, oppressed queer young woman of color without having to actually work with queer women of color, Miquela espouses vague messages about equality while simultaneously commodifying social progress for capital gain. Miquela represents only one example of how we have given ourselves permission to give up. (Boshier 2020)
Brud also makes Bermuda, a highly sexualized Caucasian woman who supports Trump. It seems clear that one company cannot authentically hold two such opposing viewpoints; the only reason to do so is to engage different marketing demographics for material gain.
Shudu, on the other hand, while engendering some upset over the fact that she was produced by a white man (“Photographer Gets Accused Of Racism” 2018), has, I argue, contributed positively to discussions about diversity in fashion. Cameron James-Wilson says in an interview, “Just the same as in many industries, the 3D world is sorely lacking ethnic diversity and black characters and assets are particularly rare. There’s a push to shift this, and with the advancement of tech and 3D industries, we can expect a change. But it’s one thing that Shudu is contributing to in her own way. It wasn’t something intentional from the start, but now I’m very interested in helping to create the resources needed for game developers and 3D designers to make more diverse characters.” (“Shudu, the First Digital Supermodel” 2018) In Shudu’s most recent Instagram post, she is seen with real-life model Alexandra-Maleek who looks like her twin. Shudu also wears clothing and jewelry by Black designers and links to their Instagram pages. In doing so, Shudu is able to highlight human talent that may be otherwise marginalized in the fashion world.

This brings me to my last point, which is that in order for virtual influencers to contribute to healthy communities, they should engage in healthy communication with humans. One disturbing trend I noticed, primarily on Miquela’s posts, was the number of conversations between bots. Constructive community is built through human-human communication, which bots can facilitate but not replace. As noted above, Shudu links to real models and designers, bringing them into conversation with each other. When Bermuda and Miquela exchange a string of comments, it may be briefly entertaining, but it is not substantive. Hatsune Miku, a Japanese virtual singer originally released in 2007, almost a decade before the US-based bots, has constructed a vibrant community around her persona. Hatsune Miku holds physical concerts around the world using a projection of her avatar, but she does not play her own music. Instead, she performs thousands of songs written by fans using software that mimics her voice. Hatsune Miku’s fans share songs and fan art with each other, often riffing off each other’s work. Hatsune Miku gathers people and provides a starting point for connection (Wikipedia). It is important that humans connect through robots, and that robots do not simply create a world for themselves.

The diversity of virtual influencers shows us that they cannot be cast off as all good or all bad. The implementation matters. If done well, virtual influencers can be valuable members of a community. In this scenario, they are honest about their non-human status, tend towards art over advertising, handle their adopted identity with grace, and facilitate connection between humans. If done poorly, they can cause upset and feelings of betrayal as well as actual harm to marginalized communities. In the worst case, they profit off of the bodies of people who have historically been oppressed and facilitate bot-bot conversations as a way to gain followers. I am hopeful we can push for a world that includes wonderful, interactive robots who delight and connect us and that don’t exist to sell us products.
References
💖 website_copy_wip_for_all_my_qtz 💖. (n.d.). Brud. Retrieved March 29, 2020, from https://docs.google.com/document/d/1V5N5tcfm7wBuUshgrmIOz9ijAO-VRqvkUbGRu0uKdI8/edit?usp=embed_facebook
B, S. (2019, December 28). 5 Cool CGI Influencers You Should Follow on Instagram. Beebom. https://beebom.com/cool-cgi-influencers-instagram/
Boshier, R. (2020, January 28). Lil Miquela Is a Queer Woman of Color. Too Bad She Isn’t Real. Bitch Media. https://www.bitchmedia.org/article/who-is-lil-miquela-racial-implications-of-simulated-influencers-of-color
Gorsler, F. (2018, February 5). Meet Fashion’s First Virtual Instagram Influencer: Lil Miquela. High Snobiety. https://www.highsnobiety.com/p/lil-miquela-virtual-influencer-instagram/
Hatsune Miku. (2020). In Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Hatsune_Miku&oldid=947415485
Hiatt, B., & Hiatt, B. (2020, March 5). Grimes: Live From the Future. Rolling Stone. https://www.rollingstone.com/music/music-features/grimes-rolling-stone-digital-cover-960843/
Hidrėlėy. (2018). Photographer Gets Accused Of Racism After His Perfect Black Model ‘Shudu’ Gets Instagram Famous. Bored Panda. https://www.boredpanda.com/3d-black-model-shudu-cameron-james-wilson/
Holmes, E. (2018, July 2). Do Avatars Make the Perfect Influencers? ELLE. https://www.elle.com/culture/a21272102/almost-human-july-2018-miquela-shudu-profile/
Katz, M. (2018, May 1). CGI ‘Influencers’ Like Lil Miquela Are About to Flood Your Feeds. Wired. https://www.wired.com/story/lil-miquela-digital-humans/
Lil Miquela. (2020). In Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Lil_Miquela&oldid=947002032
Morency, C. (2018, February 5). Meet Fashion’s First Computer-Generated Influencer. Business of Fashion. https://www.businessoffashion.com/articles/intelligence/meeting-fashions-first-computer-generated-influencer-lil-miquela-sousa
Petrarca, E. (2018, April 18). A Pro-Trump Troll Hacked Instagram’s Favorite Virtual Influencer. The Cut. https://www.thecut.com/2018/04/lil-miquela-hack-instagram.html
Princess of South Africa Barbie Doll. (n.d.). Retrieved March 29, 2020, from https://barbie.mattel.com/shop/en-us/ba/barbie-dolls-of-the-world/princess-of-south-africa-barbie-doll-56218
Remsen, N. (2016, May 2). Riccardo Tisci Gives Japan’s Biggest Virtual Virtuoso an Haute Couture Makeover. Vogue. https://www.vogue.com/article/riccardo-tisci-hatsune-miku-haute-couture-makeover-avatar
Shieber, J. (2019, January 14). More investors are betting on virtual influencers like Lil Miquela. TechCrunch. http://social.techcrunch.com/2019/01/14/more-investors-are-betting-on-virtual-influencers-like-lil-miquela/
Shudu, the First Digital Supermodel: What You Need to Know. (2018, March 5). Highsnobiety. https://www.highsnobiety.com/p/shudu-digital-supermodel/
Soul Machines—Changing the Face of AI. (n.d.). Soul Machines. Retrieved March 28, 2020, from https://www.soulmachines.com/
Thiyagarajan, D. (2020, February 10). Inside The Mind Of Singapore’s First Virtual Influencer, Audy Bleu. RICE. https://www.ricemedia.co/culture-people-singapore-first-virtual-influencer-audy-bleu/
Wright, M. (2019, April 13). KFC unveils hot CGI “virtual influencer” as their new Colonel Sanders. Mail Online. https://www.dailymail.co.uk/news/article-6918277/KFC-unveils-hot-virtual-influencer-Colonel-Sanders-recipe-tattoo-chiseled-ab.html
1 reply on “A New Bot on the Block: The Rise of Virtual Influencers and What It Means for Our Online Communities”
Digital influencers are a fascinating phenomenon, and absolutely worth examination. It’s interesting to me that the healthiest of the communities you mention here is one you only scratch the surface of – Hakune Mitsu. I’m curious where you see the community to be around Lil Miquela, for instance – is it the group of people debating questions of race and agency around her? Or is it the (very small) community of people who are creating these presences and interacting them with one another? It’s a fascinating place to dig, but I’d love to see more work exploring where an individual artist’s creation ends and community begins.