Abstract
“They are transmissions sent from isolation, like radio diaries from a stranded spacecraft.”(1)
In a time of global pandemic and extreme social isolation, the messages are not interstellar radio waves. Rather, the transmissions in question are recipes.
Online spaces for cooking are reminiscent of the early days of the internet; when most of online interaction was just about reveling in the simple joy of meeting others who are also interested in whatever topic you are discussing online. As a space for communal gathering and sharing about food, the New York Times (NYT) Cooking website is an exemplary example of a healthy online community. The NYT Cooking website’s comments section is so uniquely wholesome and candid that it even has its own dedicated Instagram (@nytcookingcomments) with 82.7k followers, highlighting hilarious comments that allow viewers to briefly peer into the lives of others through the vehicle of recipes. In the time of COVID-19, cooking has also adapted to become a form of community and resilience; a solace that can only be found online in times when physical interaction is prohibited. Examples of healthy online communities can be found on Chinese social media cooking website, Xiachufang. Even in extreme situations, people are gathering online to show how they are preparing meals at home during the period of mandated quarantine by sharing their recipes and techniques with others.
Keywords: cooking, recipes, New York Times Cooking, COVID-19, healthy communities, social media, quarantine cuisine
Literature Review
The most dreaded place for many corners of the internet is often: the comments section. A brief scroll through many a popular comments-enabled webpage can show the hurtful and crude content that seems inherent to any public post. A healthy online community exemplifies moments for community members to connect in meaningful and constructive ways. Spaces for civil discourse; places where individuals can share, disagree and discuss with civility and mutual respect, feel increasingly difficult to encounter on the internet.
Among adult American internet users, “73% [of users] had seen someone being harassed online, such as by being called offensive names or purposefully embarrassed, and 40% had personally experienced online harassment. Of those who had experienced it directly, 66% reported that the most recent incident had occurred on social media, often Facebook, and 22% said that it had occurred in a website’s comments section. Moreover, such negative online experiences appear to be worsening. According to the most recent Civility in America report, the proportion of Americans who expected further deterioration in civility increased from 39% in 2010 to 56% in 2016 (Weber Shandwick et al., 2017).”(2)
Despite the apparent lack of it in social media, civility in discourse is a crucial part of democratic deliberation and a critical symbol of “a developed democratic society.”(3) A unique case study on a corner of the internet where almost all comments are constructive and dare I say it, funny, can be found in the comments section of the New York Times (NYT) Cooking website. This case study was researched during the rise of COVID-19 in the United States, arriving after causing extensive practices of social distancing in China. A comparative case study between the NYT Cooking community and the phenomenon of “quarantine cuisine” communities on Chinese social media further illustrate the genre of online cooking communities as a unique haven from uncivil community behavior, even during extreme times.
Comparative Case Studies
Case Study 1: New York Times Cooking
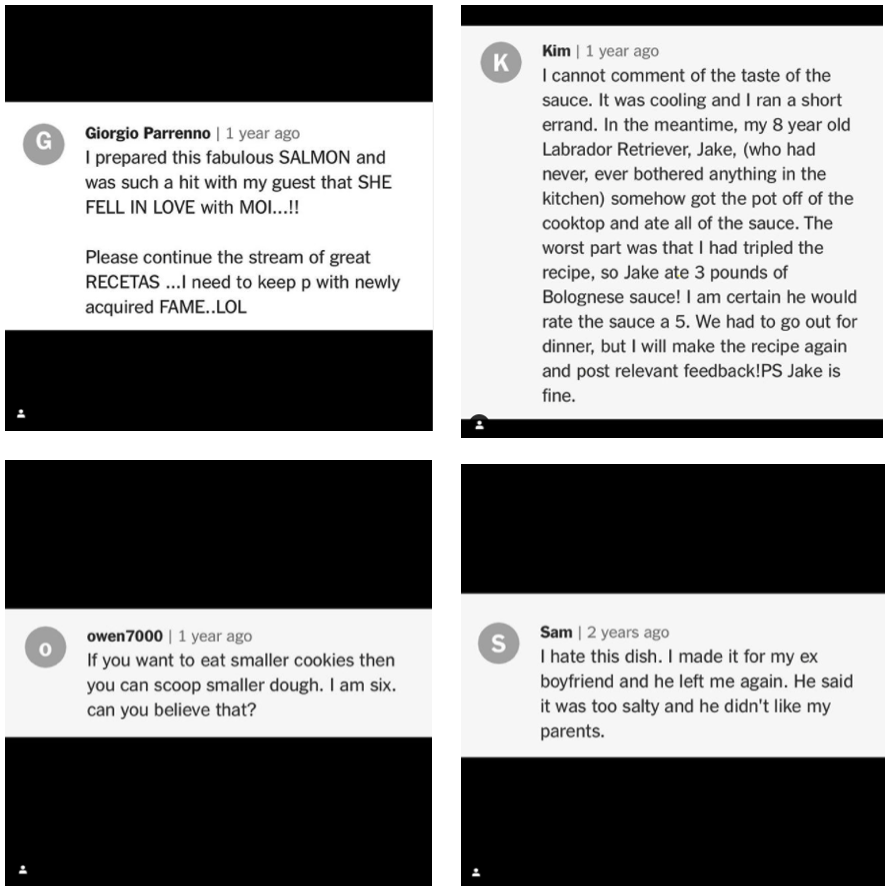
One of the website’s most famous comments on NYT Cooking can be found under the recipe for “Katharine Hepburn’s Brownies”:
“This has been my go-to brownie recipe for 30 years, even after going to baking school! I agree that using the best cocoa possible makes a difference. These days, I use Callebaut. In the 80s, an acquaintence in Germany to whom I brought some of the brownies, and who considered herself a great cook, asked for the recipe but was never able to get it to work. She kept asking me what she was doing wrong and I was never able to solve her problem. Eventually, she moved to the US and stole my husband!”(4)
These vignettes of micro-dramas peppered throughout the NYT Cooking comments section are humanizing moments on the internet. The act of cooking is deeply personal and subjective. “A recipe about cookies might conjure up feelings about your upbringing — be them happy, sad, or in between. How you might’ve been taught to make, say, macaroni and cheese (a pretty divisive dish itself, especially when it comes to the best cheese, consistency, and toppings) can affect how you feel about a particular recipe found on the internet as well. Which is perhaps why people tend to get so territorial about certain ingredients or instructions, or get so emotionally invested to the point they feel the need to tell you everything that happened leading up to and after completing a recipe. The nature of cooking is deeply personal and cultural, reflecting our age, gender, where we come from, and a whole host of our identities.” (5)
The affordances that are designed in the interactions available to users provide moments for constructive discourse. According to NYT Food editor Sam Sifton, when NYT Cooking was founded, “we made a conscious decision to call for recipe ‘notes’ instead of ‘comments.’ We know people feel strongly about the recipes we run, and we’re happy to read and share what they have to say, but we want the site to be really and truly useful to readers. We felt that asking for ‘notes’ on recipes would lead to a more collegial and fact-based atmosphere than one filled with mere comment and opinion. That’s worked to a large extent.”
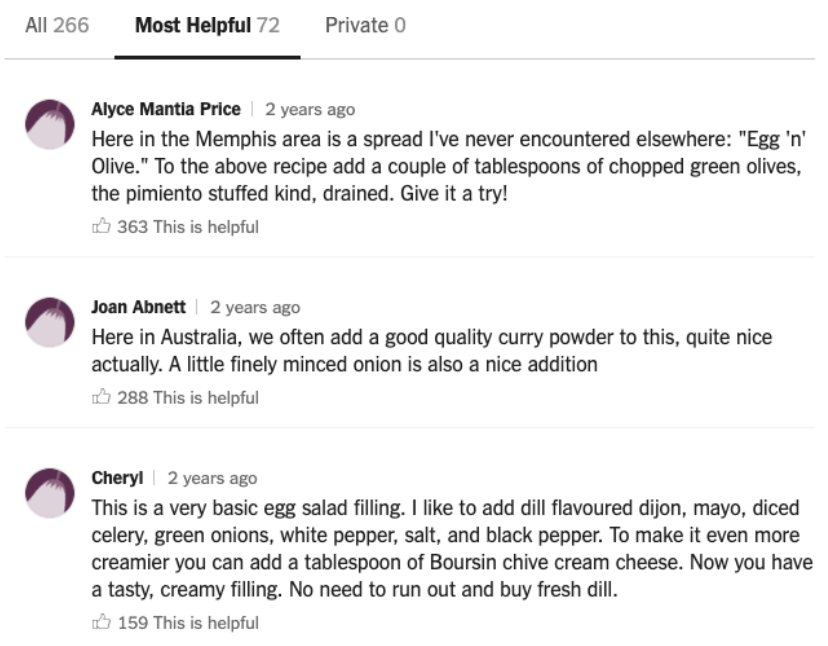
For instance, under the “Eli Zabar’s Egg Salad Sandwich” recipe (image on the left), Alyce and Jean each contribute their local perspectives from Memphis and Australia, respectively. By framing a comment as a “note,” NYT Cooking invites members to contribute constructive feedback towards achieving a better constructed dish. Members can “upvote” by marking comments as helpful, bringing those comments forward in the “Most Helpful” section which is featured as the default column shown while scrolling through a recipe.

Under Mark Bittman’s “Lemon Souffle” recipe, the top comment comes from Christopher Johnson, who writes “So light and fluffy it feels like a tangy cloud! My wife hates me and life is meaningless. Be sure to be careful with the variety of lemon because it can sometimes be too tart. Good luck!”(8) Comments like Christopher’s and the responses below like these remind us of what makes the internet great. In this forum, we are reminded of “what cooking is all about — perhaps because food is such a visceral, basic, universal need, so tied up in our memories and emotions, from romantic passion to sadness to downright anger. Recipe communities can feel like a safe space in which to vent.”(9) No matter how anxiety-inducing the world around us can be, after a long day, we can always hope to step into our kitchen and make a bit of food that reminds us of somewhere, a childhood memory or a wonderful time shared with friends. By connecting with others online to find ways to find out how to crowdsource the best way to make a meal, we share a common goal and on the internet, find that there really are others that share in this humanity as well.
Case Study 2: Xiachufang
During the rise of COVID-19 in China, 780 million Chinese citizens were cited to have been practicing social distancing and staying home. (10) “Stuck at home because of China’s tough measures to rein in the spread of a coronavirus, millions of people are discovering an unexpected interest in cooking, with restaurants closed nationwide. Downloads of the top five recipe apps more than doubled in February to 2.25 million at China’s app stores, such as Xiachufang, from January’s 1 million, said research firm Sensor Tower.” (11) Zhang Xuesi, a popular chef on the Xiachufang recipe platform describes the rise in popularity of Xiachufang as a place that gives “learners an emotional outlet beyond just aspects of cooking,” whereas in the past, “users were only interested in learning cooking tricks, but now we talk about all kinds of subjects.”(11)

Google translated comments below the “Invincible Tofu” recipe on Xiachuafang.
Beijing-based journalist and comic book artist Krish Raghav describes Xiachufang as a place where in the absence of being able to meet in real life, “people are posting daily diaries as coping mechanism,” and posting recipes as “diaries as a way of saying ‘I’m surviving, I’m still here.’” (12) A collaborative meeting of people over the internet to share not just recipes, but tips on how to adapt with limited access to ingredients and “overabundance of time” at home.

User Wu Shuang stayed home in Beijing for the month of February, and while learning how to prepare meals at home, “besides watching cooking shows, she reads users’ comments to learn from their mistakes, she said, with the only downside of her experiments being the washing up afterwards.”(11) By meeting online, people are able to deal with social isolation by connecting without the public-health risk of meeting in person. In times of extreme social isolation, the simple pleasure of encountering others online and sharing in their company over the discussion of preparing food is reminiscent of the way digital communities were in the early days on the internet.
Conclusion
A community is defined as “a feeling of fellowship with others, as a result of sharing common attitudes, interests, and goals.” A healthy online community is a digital space for members to share their perspectives and personal narratives towards a welcoming and inclusive community. Online spaces for cooking such as NYT Cooking exemplify characteristics for healthy online communities. Members contribute their “notes” as if striving to collectively create a definitive “best” recipe for a certain dish. In their notes, members also share private moments and memories that are revealing in the deeply personal ritual of cooking. As a comparative case study, recipe website Xiachufang also stands the test of what it means to be a healthy online community, weathering trying times together by sharing stories of food and survival at home during the rise of COVID-19. In a time when civility can seem significantly lacking online, finding an online community convening in the comments section with not just civil but helpful and hilarious comments feels like a beacon of hope for the future of online communities. By gathering and engaging in civil discourse about something as beautiful and simple as an egg salad sandwich, we can perhaps begin to re-learn ways to discuss and engage with others online.
Works Cited:
1.“Quarantine Cooking: Finding Relief from Coronavirus Anxiety in the Kitchen | The New Yorker,” February 29, 2020. https://web.archive.org/web/20200229060017/https://www.newyorker.com/culture/cultural-comment/quarantine-cooking-finding-relief-from-coronavirus-anxiety-in-the-kitchen.
2. Su, Leona Yi-Fan, Michael A Xenos, Kathleen M Rose, Christopher Wirz, Dietram A Scheufele, and Dominique Brossard. “Uncivil and Personal? Comparing Patterns of Incivility in Comments on the Facebook Pages of News Outlets.” New Media & Society 20, no. 10 (October 1, 2018): 3678–99. https://doi.org/10.1177/1461444818757205.
3. Boatright, Robert G., Timothy J. Shaffer, Sarah Sobieraj, Dannagal Goldthwaite Young, Timothy J. Shaffer, Sarah Sobieraj, and Dannagal Goldthwaite Young. A Crisis of Civility? : Political Discourse and Its Discontents. Routledge, 2019. https://doi.org/10.4324/9781351051989.
4. Times, The New York. “Katharine Hepburn’s Brownies Recipe.” NYT Cooking. Accessed March 26, 2020. https://cooking.nytimes.com/recipes/10782-katharine-hepburns-brownies.
5. Taylor Bryant, “A Good Place: The Only Good Comments Section on the Internet,” The Outline, accessed March 5, 2020, https://theoutline.com/post/8393/a-good-place-nyt-cooking-comments.
6. “New York Times Recipe Commenters (Politely) Spill Their Guts – The New York Times.” Accessed March 26, 2020. https://www.nytimes.com/2017/10/11/reader-center/new-york-times-recipe-commenters-politely-spill-their-guts.html.
7. Elaine Louie, “Eli Zabar’s Egg Salad Sandwich Recipe,” NYT Cooking, accessed March 25, 2020, https://cooking.nytimes.com/recipes/1013506-eli-zabars-egg-salad-sandwich.
8. Bittman, Mark. “Lemon Soufflé Recipe.” NYT Cooking. Accessed March 29, 2020. https://cooking.nytimes.com/recipes/1015594-lemon-souffle.
9. “New York Times Recipe Commenters (Politely) Spill Their Guts – The New York Times.” Accessed March 26, 2020. https://www.nytimes.com/2017/10/11/reader-center/new-york-times-recipe-commenters-politely-spill-their-guts.html.
10. CNN, James Griffiths and Amy Woodyatt. “780 Million People in China Face Travel Restrictions over Coronavirus Outbreak.” CNN. Accessed March 29, 2020. https://www.cnn.com/2020/02/16/asia/coronavirus-covid-19-death-toll-update-intl-hnk/index.html.
11. “Cooped up by Coronavirus, Millions in China Discover the Joy of Cooking – Reuters.” Accessed March 29, 2020. https://www.reuters.com/article/us-health-coronavirus-china-cooking/cooped-up-by-coronavirus-millions-in-china-discover-the-joy-of-cooking-idUSKBN2100XS.
12. ABC Radio National. “The Emerging World of ‘Quarantine Cuisine.’” Sound, March 6, 2020. https://www.abc.net.au/radionational/programs/blueprintforliving/quarantine-cuisine/12027768.

1 reply on “Case Study: Comparative Observations of Online Spaces for Cooking”
This is a really excellent piece of work. You’ve identified two case studies that share a common purpose and a moment in time – cooking during COVID – and done an excellent job of identifying the ways a platform designed for one sort of conversation supports other kinds of conversation. I’m curious as to whether there’s more to learn in this case study from contrast. Did you find significant differences between the NYT and Xiachufang? Does the fact that NYTimes is a closed (and pricey!) community lead to different dynamics than more open communities? I’ll also be interested to see whether these communities transform at al after we are no longer distancing – is this a moment in time or a deeper dynamic made possible by cooking as a deeply emotional practice? Great work.